Caching is one of the important aspect when we do system design as it enhance the performance.
In many of my applications I have used Ehcache as a cache provider with Spring applications. One of the problem with Ehcache is ; the cache resides in Single Node.
Let's consider the below scenario:
Suppoe, we have an application where we have a method which provides Book details based on isbn provided in input. The method to findBookByIsbn is costly & cache is implemented.
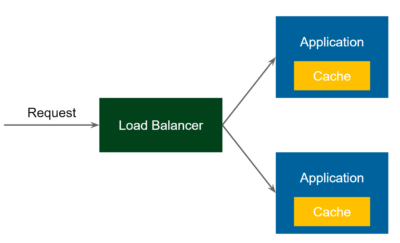
Now, we call findBookByIsbn for isbn 1 & through Load Balancer, it goes to Node 1 & it fetches the data from DataBase & store in cache.
Now, another call is made to findBookByIsbn for isbn 1 & through Load Balancer, it now goes to Node 2. In this case it again fetches the data from DataBase & store in cache.
Hence, for same data (isbn=1) the db call is again made in DataBase as the cache resides in each node seperately.
The architecture is deplicted in below image
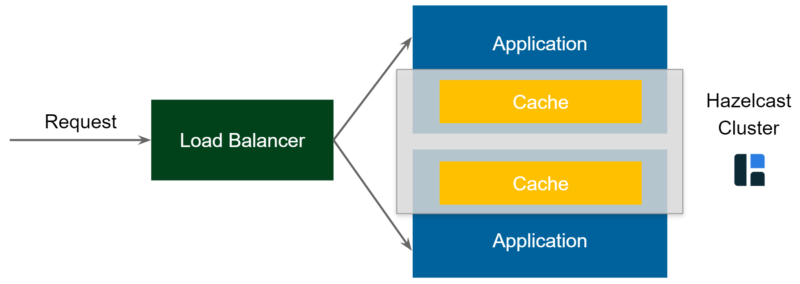
Now, you can solve this problem by creating an Embedded Distributed Cache (aka Replicated Cache). In this case, Cache of Node 1 interacts with Node 2 & replicates the data. The architecture will look like below:
This technique can be implemented using Ehcache with JGroups.
EHCache Replicated Cache Tutorial Links:
As in Ehcache-Jgroups combination, we need to do lot of manual configuration, another good alternative is using Hazelcast. In this note, I am going to give you the steps you required to use HazelCast as cache manager
Pre-requisite:
Requied Java Version: 8
Spring Framework Verion used: 4.3.30.RELEASE
The Cache data type should implement Serializable interface
Step #1: Adding Maven dependency for Hazelcast Spring integration & Spring Context upport
<dependency>
<groupId>com.hazelcast</groupId>
<artifactId>hazelcast-spring</artifactId>
<version>4.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>4.3.30.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
Step #2: Defing the method. The method must be defined in a Spring Bean class (Class having annotation Service/Component or defined in XML)
@Cacheable("bookIsbnCache")
public Book findBookByIsbn(String isbn) {
// DB / Service call goes here
}
Step #3: Define the cache in application context xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache"
xmlns:hz="http://www.hazelcast.com/schema/spring"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache.xsd
http://www.hazelcast.com/schema/spring
http://www.hazelcast.com/schema/spring/hazelcast-spring.xsd">
<!-- Other bean definition-->
<cache:annotation-driven
cache-manager="cacheManager" />
<hz:hazelcast id="instance">
<hz:config>
<hz:cluster-name>TestHzCluster</hz:cluster-name>
<!-- used for clustering.
<hz:network port="5701" port-auto-increment="false">
<hz:join>
<hz:multicast enabled="false" />
<hz:tcp-ip enabled="true">
<hz:members>x.x.x.x, y.y.y.y</hz:members>
</hz:tcp-ip>
</hz:join>
</hz:network>
-->
<hz:map name="bookIsbnCache" time-to-live-seconds="60"
in-memory-format="BINARY">
<hz:eviction eviction-policy="LRU"
max-size-policy="PER_NODE" size="100" />
</hz:map>
</hz:config>
</hz:hazelcast>
<bean id="cacheManager"
class="com.hazelcast.spring.cache.HazelcastCacheManager">
<constructor-arg ref="instance" />
</bean>
</beans>
That' it. You can deploy your code in different ports in localhost & you will be able to see the cache is replicated among differnt nodes.
Below is the link for working demo:
https://github.com/souravdalal/SpringHazelcastCacheDemo
Furthur Reading:
Cache Topologies:
Hazelcast with Spring Boot: